Invite collaborator : GitHub
This guide describes how to invite a GitHub user as a collaborator to a GitHub repository (repo).
If you invite a collaborator to your GitHub repo, the collaborator can modify the files in your GitHub repo. For example, as part of a review, an author might add a reviewer as a collaborator. Then, the reviewer can modify files on the author’s branch.
Note: To follow this guide you must have the required user permissions for adding collaborators to your chosen GitHub repo (or fork). As an example, this guide invites the GitHub user eamonnk as a collaborator to the GitHub fork/ repo mkavana/learn-pr. The invitation to collaborate is sent from a personal GitHub account (free/ basic). Apply this guide to any suitable GitHub username and fork/ repo by adapting the steps accordingly.
Prerequisites
Before you proceed complete the following:
- Install Visual Studio Code
- Install Docs Authoring Pack
- Install Word Count extension
- Install Pull Requests extension
- Install Azure Repos extension
- Install Git client
- Set Git credentials
- Terminology and concepts
- General project workflow
- Download course files (clone repo)
- Project branching policies
- Create new branch in VSC
- Send (push) files
- Markdown syntax guide
- Add/ edit markdown in VSC
- Add/ edit images in VSC
- Fix linter issues
Topics in this guide
Invite a collaborator to a GitHub repo
-
Open a web browser, sign at GitHub.com. Then, go to the GitHub fork/ repo you’re inviting a collaborator to at:
https://github.com/ Your GitHub username/ Your fork or repo name/. -
Select the Settings tab.
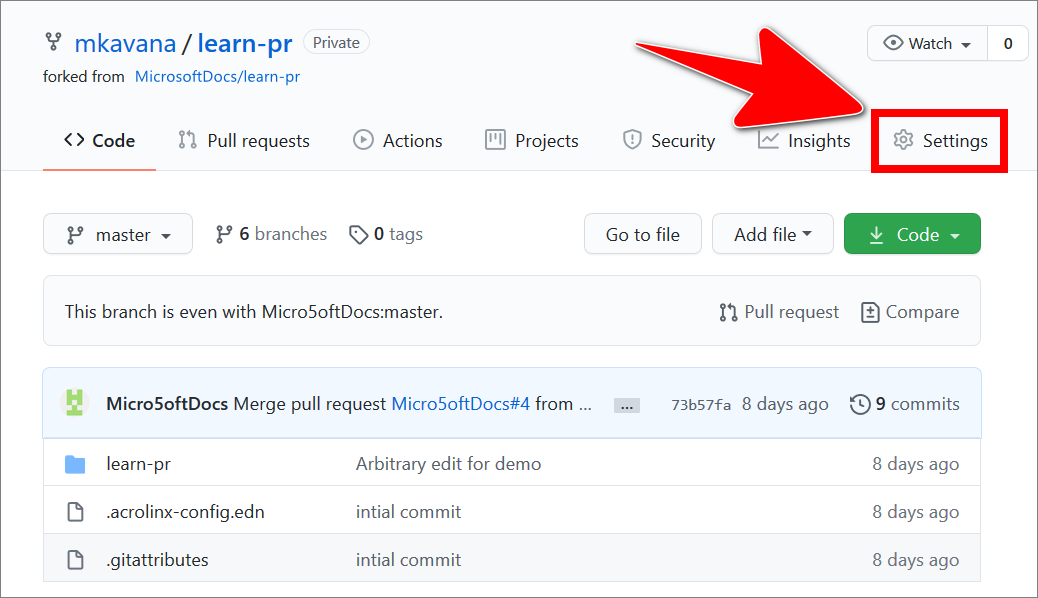
-
Choose Manage access.
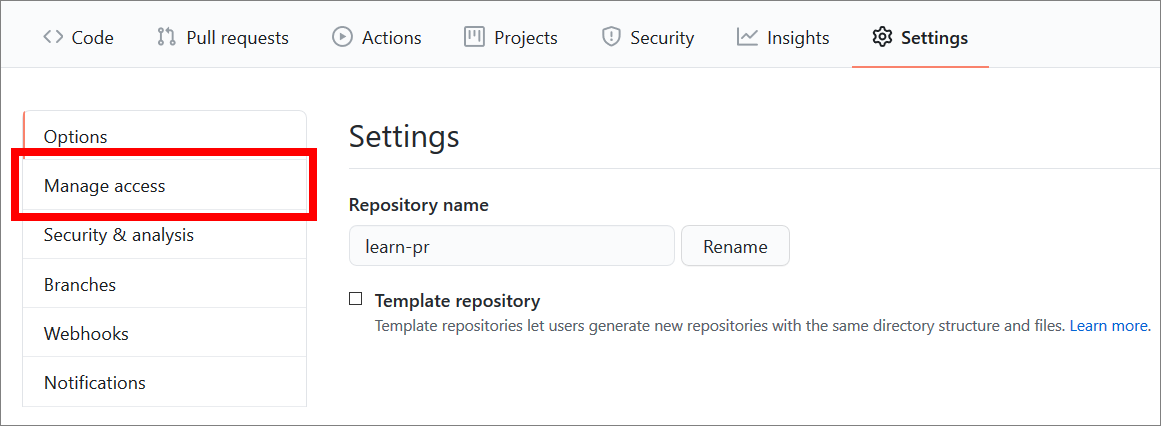
-
Select Invite collaborator.
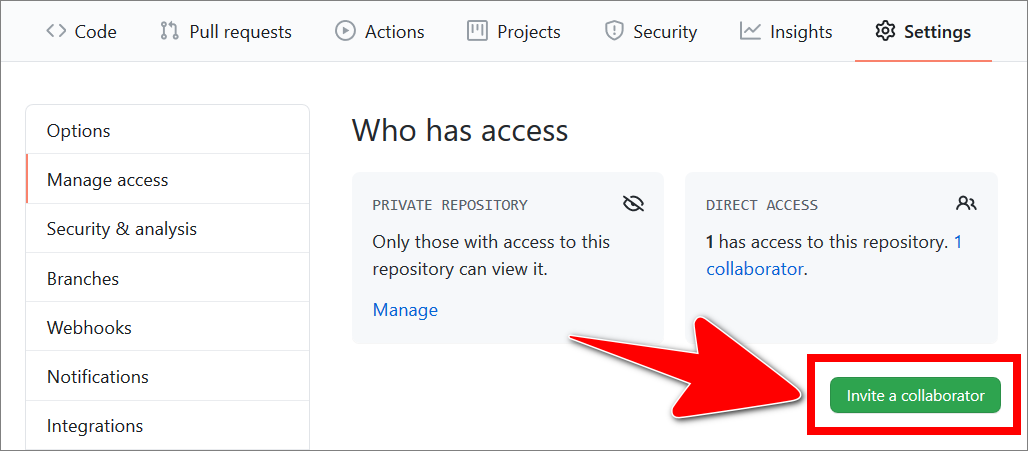
-
Enter the GitHub username you want to invite.
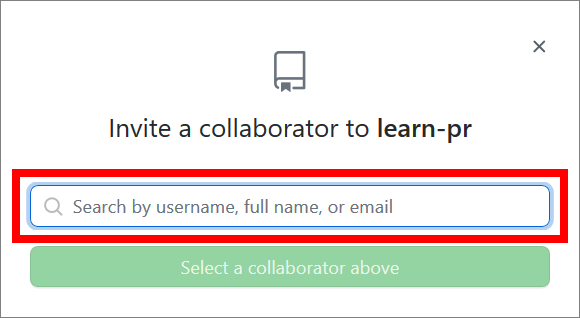
-
Select Add
usernametorepo-nameto confirm.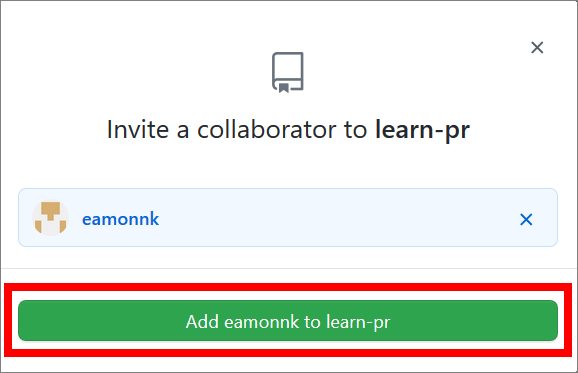
-
GitHub sends your invitation to the potential collaborator, and notifies you when the collaborator responds to your invitation.
You’ve invited a collaborator to a GitHub repo successfully.
Note: If you’ve owner or admin access permissions to a GitHub repo, you can assign read, write, or admin roles to other GitHub users. To allocate roles to users of a GitHub repo, refer to Manage collaborator access to a GitHub repo by role.
Manage collaborator access to a GitHub repo by role
If you have owner or admin level access permissions to a GitHub repo within an organization, you can allocate roles to specific GitHub collaborators. Where applicable, each role grants a collaborator different access permissions to the GitHub repo. With roles you can choose who has read (pull), write (push), or admin access to the GitHub repo.
Note: The following steps assume your invitation to add a GitHub collaborator has been accepted; refer to Invite a collaborator to a GitHub repo. You must also have owner or admin access permissions to the GitHub repo you want to manage, and the GitHub repo must be owned by an organization.
Complete the following steps to manage collaborator access to a GitHub repo by role.
-
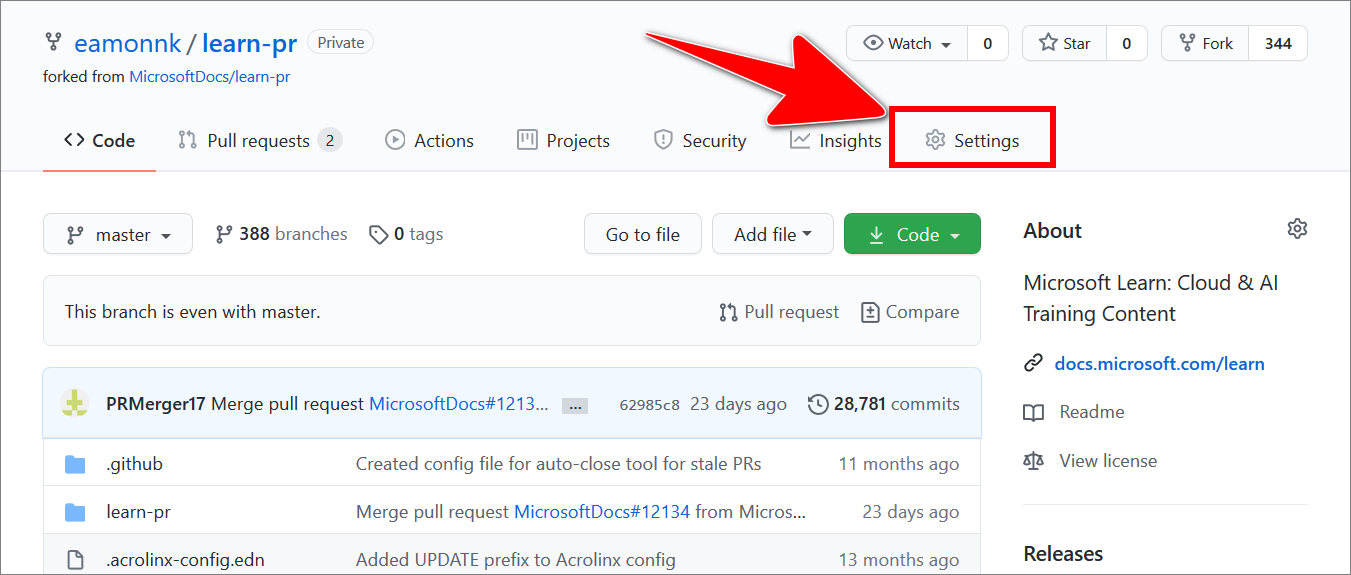
Open a web browser, sign at GitHub.com. Then, go to the GitHub fork/ repo you want to manage access to at:
https://github.com/ Your GitHub username/ Your fork or repo name/.For example, go to
https://github.com/eamonnk/learn-pr/. -
Select the Settings tab.
-
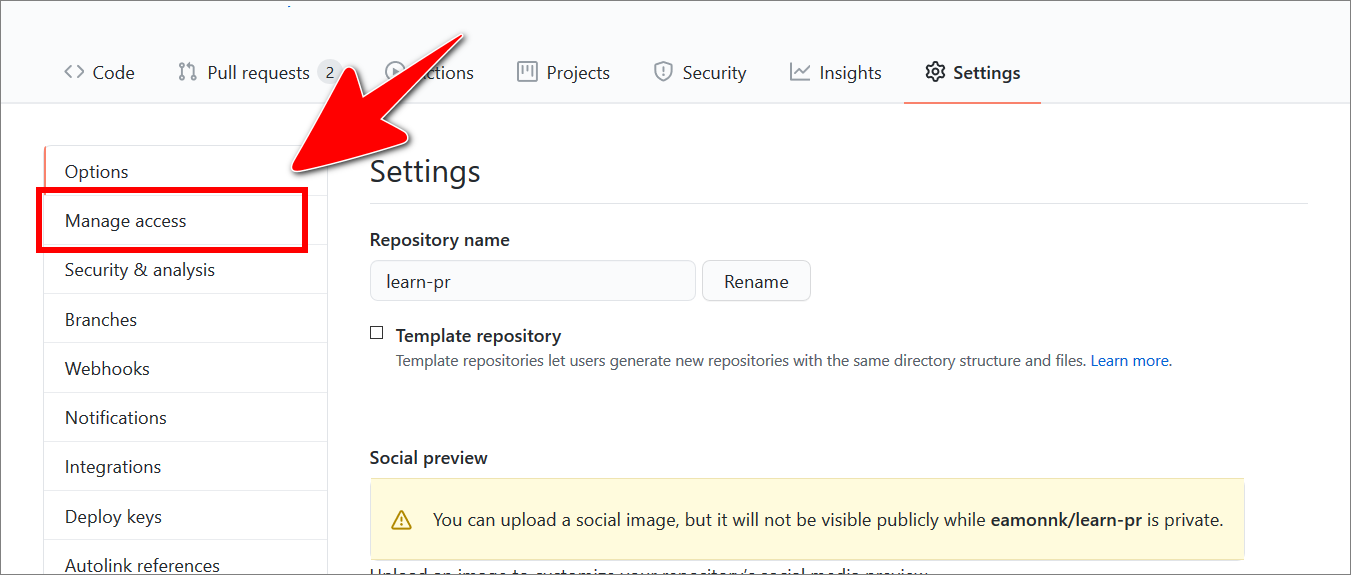
Choose Manage access.
-
Use the dropdown beside a collaborator’s GitHub username to set the user’s role.
For example, in the following image, the role Admin is set for the username mkavana.
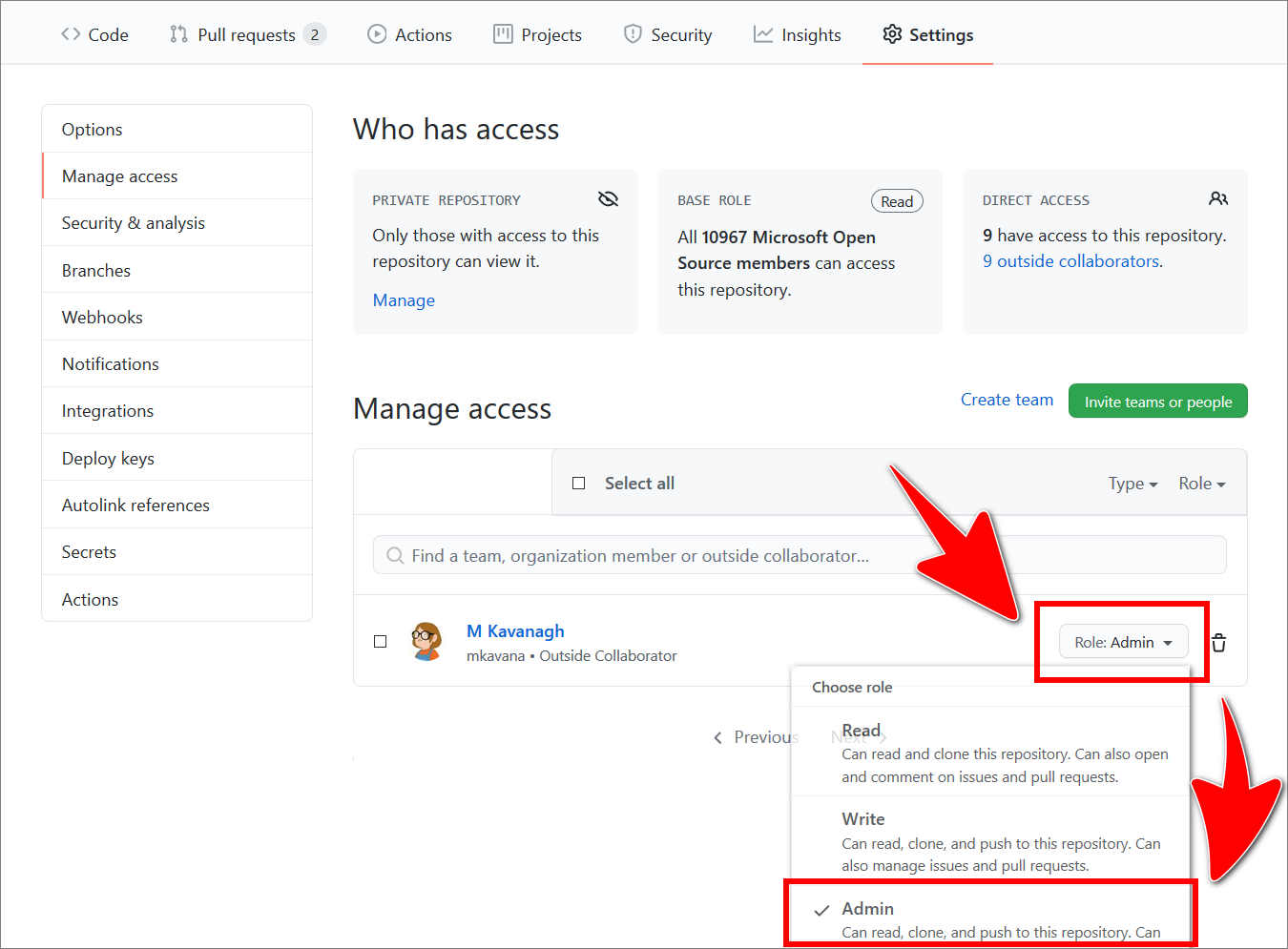
The following table describes each role.
Role Description Read Can read and clone this repository. Can also open and comment on issues and pull requests. Write Can read, clone, and push to this repository. Can also manage issues and pull requests. Admin Can read, clone, and push to this repository. Can also manage issues, pull requests, and repository settings, including adding collaborators.
You’ve managed collaborator access to a GitHub repo by role successfully.
Note: For information about managing access by role for a GitHub repo, refer to Repository permission levels for an organization.
Appendices
Check the following supplementary Appendices for more details and context.
